He can’t record the entire expense when it is paid because some of it was already recorded. If the accountant did not make a reversing entry at the beginning of the year, the accountant will have this entry upon collection of the income. What was debited is now credited and what was credited is now https://www.bookstime.com/ debited. If we run a Profit and Loss (P&L, also known as an Income Statement) for November only, we should see a wage expense of $3,800. That expense is the total of the November 25 pay for the first half of the month, and the December 10 payroll that we accrued for the second half of the month.
The 4 Factors of Production of a Business
The goal of the reversing entry is to ensure that an expense or revenue is recorded in the proper period. If the loan is issued on the sixteenth of month A with interest payable on the fifteenth of the next month (month reversing entries are optional B), each month should reflect only a portion of the interest expense. To get the expense correct in the general ledger, an adjusting entry is made at the end of the month A for half of the interest expense.
![]()
AccountingTools
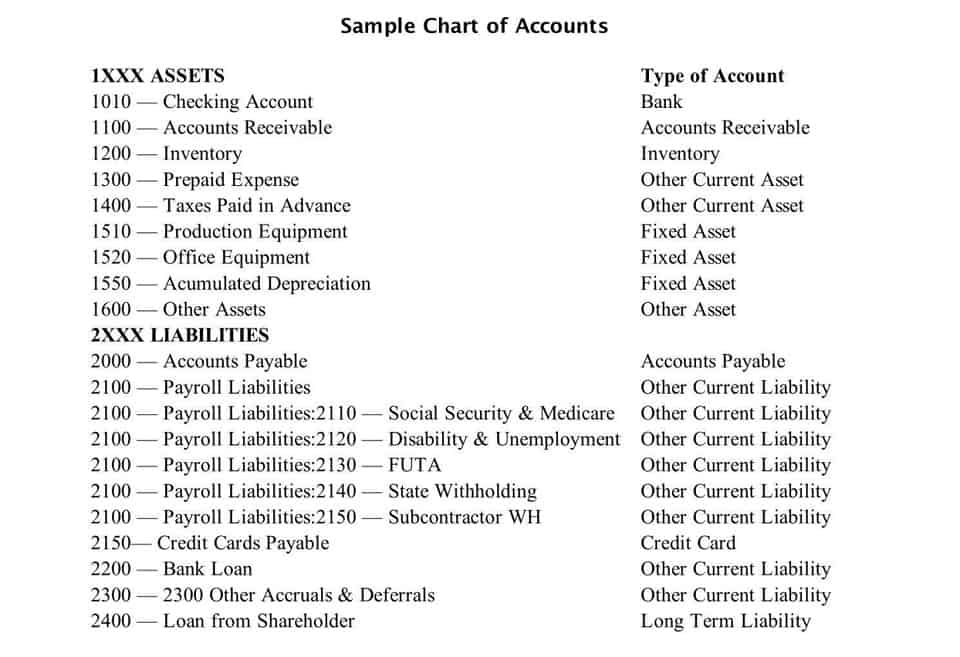
A trial balance is prepared to test the equality of the debits and credits. All account balances are extracted from the ledger and arranged in one report. The process nonetheless does not end with the presentation of financial statements.
Accounting with the reversing entry:
- As before, in month 2, wages of 4,000, which includes the 1,500 from month 1, are paid, and the following journal is made.
- If the actual invoice is $18,000 the balance in Temp Service Expense will change from a credit balance of $18,000 to a balance of $0.
- While you might have been well-intentioned in deleting incorrect journal entries, it’s better to lay your cards out to auditors by showing them your erroneous and corrective journal entries.
- For example, on the first payday following the reversing entry, a “normal” journal entry can be made to record the full amount of salaries paid as expense.
- You’d then have to do some accounting and arithmetic gymnastics to record the $9,500 invoice accurately.
- Reversing entries are prepared and posted to the ledger on the first day of the succeeding accounting period, even though they are the last step in the accounting cycle.
As the name suggest, reversing entry is recorded by reversing the accounts nature. All of the debits and credits accounts are recorded as contra debits and credits with the same amount to “nullifying” the accounting impact. In other words, the accounts with debit nature will be credited by the same amount in the reversing entries. Adjusting entries are prepared as an application of the accrual concept of accounting.
NeatNick’s balance sheet at the end of the month will show that the company owes the employees $2,200, which we will pay on December 10. An optional step at the beginning of the next accounting period is to record and post reversing entries. The accounting process starts with identifying and analyzing business transactions and events. Not all transactions and events are entered into the accounting system. A manual reversing entry is when you record your journal entry yourself, ensuring that you record the appropriate entries at the end of the preceding month as well.
- It is extremely easy to forget to manually reverse an entry in the following period, so it is customary to designate the original journal entry as a reversing entry in the accounting software when it is created.
- In other words, the accounts with debit nature will be credited by the same amount in the reversing entries.
- The temp agency will bill the retailer on January 6 and the retailer is required to pay the invoice by January 10.
- Since the $250 is insignificant difference from an estimated amount, it is acceptable to report the $250 as a January expense instead of a December expense.
Accounting without the reversing entry:
For example if Company X wanted to make an adjustment for $600 in unpaid wages, it would debit that amount from the wages expense account and credit it to the wages payable account. This reversing entry should decrease the prepaid insurance account by $30,000, resulting to a zero balance again, effectively reversing the adjusting entry. At the same time, the insurance expense account would be debited for $30,000 which corresponds to the unexpired portion. When reversing entries are not made, the accountant needs to remember last period adjusting entries and account for any expense/revenue previously recognized relating to current period payments or receipts. Reversing entries are passed at the beginning of an accounting period as an optional step of accounting cycle to cancel the effect of previous period adjusting entries involving future payments or receipts of cash. It should be noted that whichever method is used, the financial statements for each month will be the same.
In the accounting cycle, recording of reversing entries is the last step. Adjusting entries are made to adjust the unrecorded events while reversing entries are made to cancel out those adjusting entries accounts that are created to just support these adjustments. When making adjusting entries, you create some new accounts where no new event has actually taken place, these are made just to make accounts on accrual basis. So, reversing entries are recorded at the start of the next period and these newly created accounts are reversed to cancel out the adjusting entries effect.
Reversing Entries: Optional step at the beginning of the new accounting period
Since the unearned revenue account already reflects the correct balance on January 1, 2024, there is no need to reverse the above adjusting entry anymore. The net effect of this entry to salaries expense would be a debit balance of $7,000 since the account was first credited for $5,000 on January 1 and debited for $12,000 on January 15. The total payroll of $12,000 consists of $5,000 salaries expense recognized on December 31, 2022 and $7,000 on January 15, 2023. In part 1, we had an introduction to reversing entries and discussed examples for accrued income and accrued expense. In this part, we will cover the two other types of entries that can be reversed – unearned income and prepaid expense.
Cash Flow Statement Template
Reversing entries are optional accounting journal entries that are made at the beginning of an accounting period, to cancel adjusting entries which were made at the end of the previous accounting period. To keep your accounting records clean, you record a reversing entry on the first of the next month that turns your liability back to $0. Then, when the bill comes in for $9,500, you record a new journal entry for $9,500 in consultant fees and accounts payable.
Having an end-of-month review process can help prevent errors on your ledger. The need to prepare reversing entries for prepaid expenses depend on which method you use in recording prepayments. If the expense method is used in recording prepaid expense, reversing entries can be prepared.